포스팅 목차
o REGR_ (Linear Regression) Functions
선형 회귀 함수는
- REGR_SLOPE
- REGR_INTERCEPT
- REGR_COUNT
- REGR_R2
- REGR_AVGX
- REGR_AVGY
- REGR_SXX
- REGR_SYY
- REGR_SXY
문법
linear_regr::=
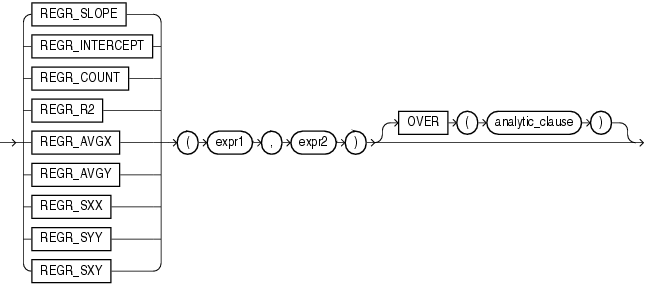
목적
- REGR_INTERCEPT : 회귀 직선의 절편 계산
- REGR_SLOPE(Y, X) : 회귀 직선의 기울기 계산
- REGR_SXX, REGR_SXY, REGR_SYY : Sxx, Sxy, Syy 제곱합
- REGR_COUNT : 회귀선 적합에 사용되는 수, 회귀선에 일치하는 null이 아닌 쌍의 개수, 회귀 선상에 찍히는 값들의 숫자를 구해준다
- REGR_R2 : 결정계수 (R-Square)
- REGR_AVGX : X의 평균
- REGR_AVGY : Y의 평균
- 기타 :: F검정 통계량, T 통계량, 자유도
선형 회귀 함수는 정규 최소 제곱 회귀 선상을 수치 쌍의 세트에 적합한다. 집계 함수와 분석함수로 이용할 수 있다.
이러한 함수는 인수로써 임의의 수치 데이터형 또는 암묵적으로 수치 데이터형으로 변환 가능한 비수치 데이터형을 취한다. 오라클은 수치 우선순위가 가장 높은 인수를 판단하여 나머지 인수를 암묵적으로 그 데이터형으로 변환하고, 그 데이터형을 반환한다.
오라클은 expr1 또는 expr2이 NULL인 모든 쌍을 제거한 후에 (expr1, expr2)을 함수에 적용한다. 오라클은 데이터를 통해 single pass 중에 동시에 모든 회귀 함수를 계산한다.
expr1은 종속변수(y 값)의 값으로 해석되고, expr2은 독립변수의 값(x값)으로 해석된다.
- REGR_SLOPE은 직선의 기울기를 반환한다. 반환 값은 수치 데이터형이고, NULL일수 있다. NULL(expr1, expr2) 쌍을 제거 후에, 다음 계산을 한다. COVAR_POP(expr1, expr2) / VAR_POP(expr2)
- REGR_INTERCEPT은 회귀 선의 y-절편을 반환한다. 반환 값은 수치 데이터형으로, NULL일수 있다. NULL(expr1, expr2) 쌍을 제거 후에, 다음 계산을 한다. AVG(expr1) - REGR_SLOPE(expr1, expr2) * AVG(expr2)
- REGR_COUNT은 회귀 직선을 적합하기 위해 이용되는 Non-Null 쌍의 수치 정수를 반환한다.
REGR_R2(은)는, 회귀에 대한 결정계수(R의 2승 또는 적합도라고도 부른다)를 되돌립니다. 반환 값은 수치 데이터형으로, NULL가 되는 경우도 있습니다. VAR_POP(expr1) 및 VAR_POP(expr2)은, NULL의 조가 배제된 후에 평가됩니다. 반환 값은 다음과 같습니다.
- REGR_R2은 회귀에 대한 결정계수(R-squared 또는 적합도)를 반환한다. 반환 값은 수치 데이터형 또는 NULL일수 있다. VAR_POP(expr1)과 VAR_POP(expr2)는 NULL 쌍 제거 후에 평가된다. 반환되는 값은 아래와 같다.
NULL if VAR_POP(expr2) = 0
1 if VAR_POP(expr1) = 0 and
VAR_POP(expr2) != 0
POWER(CORR(expr1,expr),2) if VAR_POP(expr1) > 0 and
VAR_POP(expr2 != 0- 이외의 모든 회귀 함수는 수치 데이터형과 NULL을 반환할 수 있다. REGR_AVGX(은)는, 회귀 직선의 독립변수(expr2)의 평균을 요구합니다. NULL (expr1, expr2)의 조를 배제한 후, 이 펑션은 다음의 계산을 실시합니다.
- REGR_AVGX는 회귀 직선의 독립변수(expr2)의 평균을 평가한다. NULL(expr1, expr2) 쌍을 제거한 후에 다음을 계산한다. AVG(expr2)
- REGR_AVGY는 회귀 직선의 종속변수(expr1)의 평균을 평가한다. NULL(expr1, expr2) 쌍을 제거한 후에 다음을 계산한다. AVG(expr1)
REGR_SXY, REGR_SXX, REGR_SYY는 여러 진단 통계를 계산하기 위해 이용되는 보조 함수이다.
- REGR_SXX는 NULL(expr1, expr2) 쌍을 제거 후에 다음을 계산한다. REGR_COUNT(expr1, expr2) * VAR_POP(expr2)
- REGR_SYY는 NULL(expr1, expr2) 쌍을 제거 후에 다음을 계산한다. REGR_COUNT(expr1, expr2) * VAR_POP(expr1)
- REGR_SXY는 NULL(expr1, expr2) 쌍을 제거 후에 다음을 계산한다. REGR_COUNT(expr1, expr2) * COVAR_POP(expr1, expr2)
예제
다음 예제는 샘플 테이블 sh.sales와 sh.products에 근거한다.
- 일반화 선형 회귀 예제
다음 예제는 다양한 선형 회귀 함수의 비교를 제공한다.
| Oracle Program |
SELECT s.channel_id,
REGR_SLOPE(s.quantity_sold, p.prod_list_price) SLOPE ,
REGR_INTERCEPT(s.quantity_sold, p.prod_list_price) INTCPT ,
REGR_R2(s.quantity_sold, p.prod_list_price) RSQR ,
REGR_COUNT(s.quantity_sold, p.prod_list_price) COUNT ,
REGR_AVGX(s.quantity_sold, p.prod_list_price) AVGLISTP,
REGR_AVGY(s.quantity_sold, p.prod_list_price) AVGQSOLD
FROM sales s, products p
WHERE s.prod_id=p.prod_id AND
p.prod_category='Men' AND
s.time_id=to_DATE('10-OCT-2000')
GROUP BY s.channel_id;C SLOPE INTCPT RSQR COUNT AVGLISTP AVGQSOLD
- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
C -.03529838 16.4548382 .217277422 17 87.8764706 13.3529412
I -.0108044 13.3082392 .028398018 43 116.77907 12.0465116
P -.01729665 11.3634927 .026191191 33 80.5818182 9.96969697
S -.01277499 13.488506 .000473089 71 52.571831 12.8169014
T -.01026734 5.01019929 .064283727 21 75.2 4.23809524
- REGR_SLOPE and REGR_INTERCEPT 예제
다음 예제는 판매 양과 각 회계 연도에 대한 판매 순이익에 대한 회귀 직선의 기울기와 절편을 계산한다.
| Oracle Program |
SELECT t.fiscal_year,
REGR_SLOPE(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold) "Slope",
REGR_INTERCEPT(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold) "Intercept"
FROM sales s, times t
WHERE s.time_id = t.time_id
GROUP BY t.fiscal_year;FISCAL_YEAR Slope Intercept
----------- ---------- ----------
1998 49.3934247 71.6015479
1999 49.3443482 70.1502601
2000 49.2262135 75.0287476
다음 예제는 amount_sold와 quantity_sold에 대한 회귀 직선의 누적 기울기와 누적 절편을 계산한다.
| Oracle Program |
SELECT t.fiscal_month_number "Month",
t.day_number_in_month "Day",
REGR_SLOPE(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold)
OVER (ORDER BY t.fiscal_month_desc, t.day_number_in_month) AS CUM_SLOPE,
REGR_INTERCEPT(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold)
OVER (ORDER BY t.fiscal_month_desc, t.day_number_in_month) AS CUM_ICPT
FROM sales s, times t
WHERE s.time_id = t.time_id
AND s.prod_id IN (270, 260)
AND t.fiscal_year=1998
AND t.fiscal_week_number IN (50, 51, 52)
AND t.day_number_in_week IN (6,7)
ORDER
BY t.fiscal_month_desc, t.day_number_in_month;
| Results |
Month Day CUM_SLOPE CUM_ICPT
---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
12 12 -68 1872
12 12 -68 1872
12 13 -20.244898 1254.36735
12 13 -20.244898 1254.36735
12 19 -18.826087 1287
12 20 62.4561404 125.28655
12 20 62.4561404 125.28655
12 20 62.4561404 125.28655
12 20 62.4561404 125.28655
12 26 67.2658228 58.9712313
12 26 67.2658228 58.9712313
12 27 37.5245541 284.958221
12 27 37.5245541 284.958221
12 27 37.5245541 284.958221
- REGR_COUNT 예제
다음 예제는 회계 담당자를 가지는 고객 테이블(319 총계 밖에)에서 고객의 수를 반환한다.
| Oracle Program |
SELECT REGR_COUNT(customer_id, account_mgr_id)
FROM customers;
| Results |
REGR_COUNT(CUSTOMER_ID,ACCOUNT_MGR_ID)
--------------------------------------
231
다음 예제는 1998년 4월의 각 해당일의 거래의 누적 수를 계산한다.
| Oracle Program |
SELECT UNIQUE t.day_number_in_month,
REGR_COUNT(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold)
OVER (PARTITION BY t.fiscal_month_number
ORDER BY t.day_number_in_month) "Regr_Count"
FROM sales s, times t
WHERE s.time_id = t.time_id
AND t.fiscal_year = 1998 AND t.fiscal_month_number = 4;
| Results |
DAY_NUMBER_IN_MONTH Regr_Count
------------------- ----------
1 825
2 1650
3 2475
4 3300
. . .
26 21450
30 22200
- REGR_R2 예제
다음 예제는 amount_sold와 quantity_sold의 회귀 직선의 결정 계수를 계산한다.
| Oracle Program |
SELECT REGR_R2(amount_sold, quantity_sold) FROM sales
WHERE amount_sold > 5000;
| Results |
REGR_R2(AMOUNT_SOLD,QUANTITY_SOLD)
----------------------------------
.024087453
다음 예제는 1998년 동안에 각 월에 대한 amount_sold와 quantity_sold에 대한 회귀 직선의 누적 결정계수를 계산한다.
| Oracle Program |
SELECT t.fiscal_month_number,
REGR_R2(SUM(s.amount_sold), SUM(s.quantity_sold))
OVER (ORDER BY t.fiscal_month_number) "Regr_R2"
FROM sales s, times t
WHERE s.time_id = t.time_id
AND t.fiscal_year = 1998
GROUP BY t.fiscal_month_number
ORDER BY t.fiscal_month_number;
| Results |
FISCAL_MONTH_NUMBER Regr_R2
------------------- ----------
1
2 1
3 .927372984
4 .807019972
5 .932745567
6 .94682861
7 .965342011
8 .955768075
9 .959542618
10 .938618575
11 .880931415
12 .882769189
- REGR_AVGY and REGR_AVGX 예제
다음 예제는 각 해에 대한 amount_sold와 quantity_sold에 대한 회귀 평균을 계산한다.
| Oracle Program |
SELECT t.fiscal_year,
REGR_AVGY(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold) "Regr_AvgY",
REGR_AVGX(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold) "Regr_AvgX"
FROM sales s, times t
WHERE s.time_id = t.time_id
GROUP BY t.fiscal_year;
| Results |
FISCAL_YEAR Regr_AvgY Regr_AvgX
----------- ---------- ----------
1998 716.602044 13.0584283
1999 714.910831 13.0665536
2000 717.331304 13.0479781
다음 에제는 amount_sold와 quantity_sold에 대한 누적 평균을 계산한다.
| Oracle Program |
SELECT t.day_number_in_month,
REGR_AVGY(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold)
OVER (ORDER BY t.fiscal_month_desc, t.day_number_in_month) "Regr_AvgY",
REGR_AVGX(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold)
OVER (ORDER BY t.fiscal_month_desc, t.day_number_in_month) "Regr_AvgX"
FROM sales s, times t
WHERE s.time_id = t.time_id
AND s.prod_id = 260
AND t.fiscal_month_desc = '1998-12'
AND t.fiscal_week_number IN (51, 52)
ORDER BY t.day_number_in_month;
| Results |
DAY_NUMBER_IN_MONTH Regr_AvgY Regr_AvgX
------------------- ---------- ----------
14 882 24.5
14 882 24.5
15 801 22.25
15 801 22.25
16 777.6 21.6
18 642.857143 17.8571429
18 642.857143 17.8571429
20 589.5 16.375
21 544 15.1111111
22 592.363636 16.4545455
22 592.363636 16.4545455
24 553.846154 15.3846154
24 553.846154 15.3846154
26 522 14.5
27 578.4 16.0666667
REGR_SXY, REGR_SXX, and REGR_SYY 예제
다음 예제는 샘플 sh.sales 테이블에서 각 해에 대한 amount_sold와 quantity_sold에 대한 REGR_SXY, REGR_SXX, REGR_SYY를 계산한다.
| Oracle Program |
SELECT t.fiscal_year,
REGR_SXY(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold) "Regr_sxy",
REGR_SYY(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold) "Regr_syy",
REGR_SXX(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold) "Regr_sxx"
FROM sales s, times t
WHERE s.time_id = t.time_id
GROUP BY t.fiscal_year;
| Results |
FISCAL_YEAR Regr_sxy Regr_syy Regr_sxx
----------- ---------- ---------- ----------
1998 1620591607 2.3328E+11 32809865.2
1999 1955866724 2.7695E+11 39637097.2
2000 2127877398 3.0630E+11 43226509.7
다음 예제는 amount_sold와 quantity_sold에 대한 누적 REGR_SXY, REGR_SXX, REGR_SYY를 계산한다.
| Oracle Program |
SELECT t.day_number_in_month,
REGR_SXY(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold)
OVER (ORDER BY t.fiscal_year, t.fiscal_month_desc) "Regr_sxy",
REGR_SYY(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold)
OVER (ORDER BY t.fiscal_year, t.fiscal_month_desc) "Regr_syy",
REGR_SXX(s.amount_sold, s.quantity_sold)
OVER (ORDER BY t.fiscal_year, t.fiscal_month_desc) "Regr_sxx"
FROM sales s, times t
WHERE s.time_id = t.time_id
AND prod_id IN (270, 260)
AND t.fiscal_month_desc = '1998-02'
AND t.day_number_in_week IN (6,7)
ORDER BY t.day_number_in_month;
| Results |
DAY_NUMBER_IN_MONTH Regr_sxy Regr_syy Regr_sxx
------------------- ---------- ---------- ----------
1 130973783 1.8916E+10 2577797.94
. . .
30 130973783 1.8916E+10 2577797.94
| 오라클 SQL 함수(Oracle SQL Function) 목록 리스트 링크 |
| [SQL, Pandas, R Prog, Dplyr, SQLDF, PANDASQL, DATA.TABLE] SQL EMP 예제로 만나는 테이블 데이터 처리 방법 리스트 링크 |
'오라클 게시판 > 오라클 함수' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 【오라클(Oracle) SQL 함수】 REPLACE 함수 (0) | 2021.10.20 |
|---|---|
| 【오라클(Oracle) SQL 함수】 REMAINDER 함수 (0) | 2021.10.20 |
| 【오라클(Oracle) SQL 함수】 REGEXP_SUBSTR 함수 (0) | 2021.10.20 |
| 【오라클(Oracle) SQL 함수】 REGEXP_REPLACE 함수 (0) | 2021.10.19 |
| 【오라클(Oracle) SQL 함수】 REGEXP_INSTR 함수 (0) | 2021.10.19 |





댓글